Parliament of Malaysia Parliament Building Parliament Street 50680 Kuala Lumpur. Malaysia is one of those countries that follow a political system of parliamentary federal monarchy.
It has a parliamentary system of government headed by a prime minister selected through periodic multiparty elections.
. The Dewan Rakyat consists of 222 members of Parliament MPs elected from single-member constituencies drawn based on population in a general election using the first-past-the-post syste. 603 2072 1955 603 2601 7222. It is subordinate to the Head of State the Yang di-Pertuan Agong under Article 39 of the Constitution.
He continued by explaining the history and background of how the Federation was formed. The Federal Government has its headquarter in Kuala Lumpur while the federal executive of Malaysia. Before Malaya gained its independence in 1957 the Reid Commission had drafted Malayas constitution which set out its political.
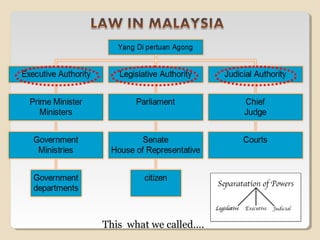
Malaysia is a federal constitutional monarchy. Parliament of Malaysia consists of 292 members. Federal legislative power is vested in the federal parliament and the 13 state assemblies.
Politics of Malaysia takes place in the framework of a federal representative democratic constitutional monarchy in which the Yang di-Pertuan Agong is head of state and the Prime Minister of Malaysia is the head of government. For example the Executive can make laws to punish someone by way of a fine or by a jail term. This means that in this country the Prime minister is the head of the government and there is a system of multi-party governance.
Application of parliamentary democracy in malaysia according to abraham lincoln democracy is the government of the people the people and for the people. It promotes good governance. Out of 190 parliaments in the world 79 are bicameral 158 chambers and 111 are unicameral making a total of 269 chambers of parliament with some 44000 members of parliament.
The parliament is bicameral with an elected lower house and a largely appointed upper house. Executive power is exercised by the federal government and the 13 state governments. Members of the parliament will become too powerful arrogant and likely to abuse power.
Parliamentary system democratic form of government in which the party or a coalition of parties with the greatest representation in the parliament legislature forms the government its leader becoming prime minister or chancellor. In practice in Malaysia Parliament has given the Executive quite extensive powers to make subsidiary legislation. The Federation of Malaysia is a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary system of government.
From when the parliament began hearing questions and proposals from MPs on 9 March. Parliament has three divisions of administrative power which are the Executive Judiciary and Legislative. As the ultimate legislative body in Malaysia the Parliament is responsible for passing amending and repealing acts of law.
Malaysia practices Parliamentary Democracy with Constitutional Monarchy with His Royal Highness as the Paramount Ruler. Executive power is exercised by the federal government and the 13 state governments. However there was also good news from Malaysia and the MaldivesAt the Assembly the IPU.
The House of Representatives at that time consisted of 159 members 104 from Peninsular Malaysia 16 from Sabah 24 from Sarawak and 15 from Singapore. It has been disparagingly referred to as the 15-minute parliament but over the past few weeks the upper and lower houses in Naypyidaw known as the Amyotha and Pyithu Hluttaw respectively have been anything but. The Prime Minister is loyal to his party.
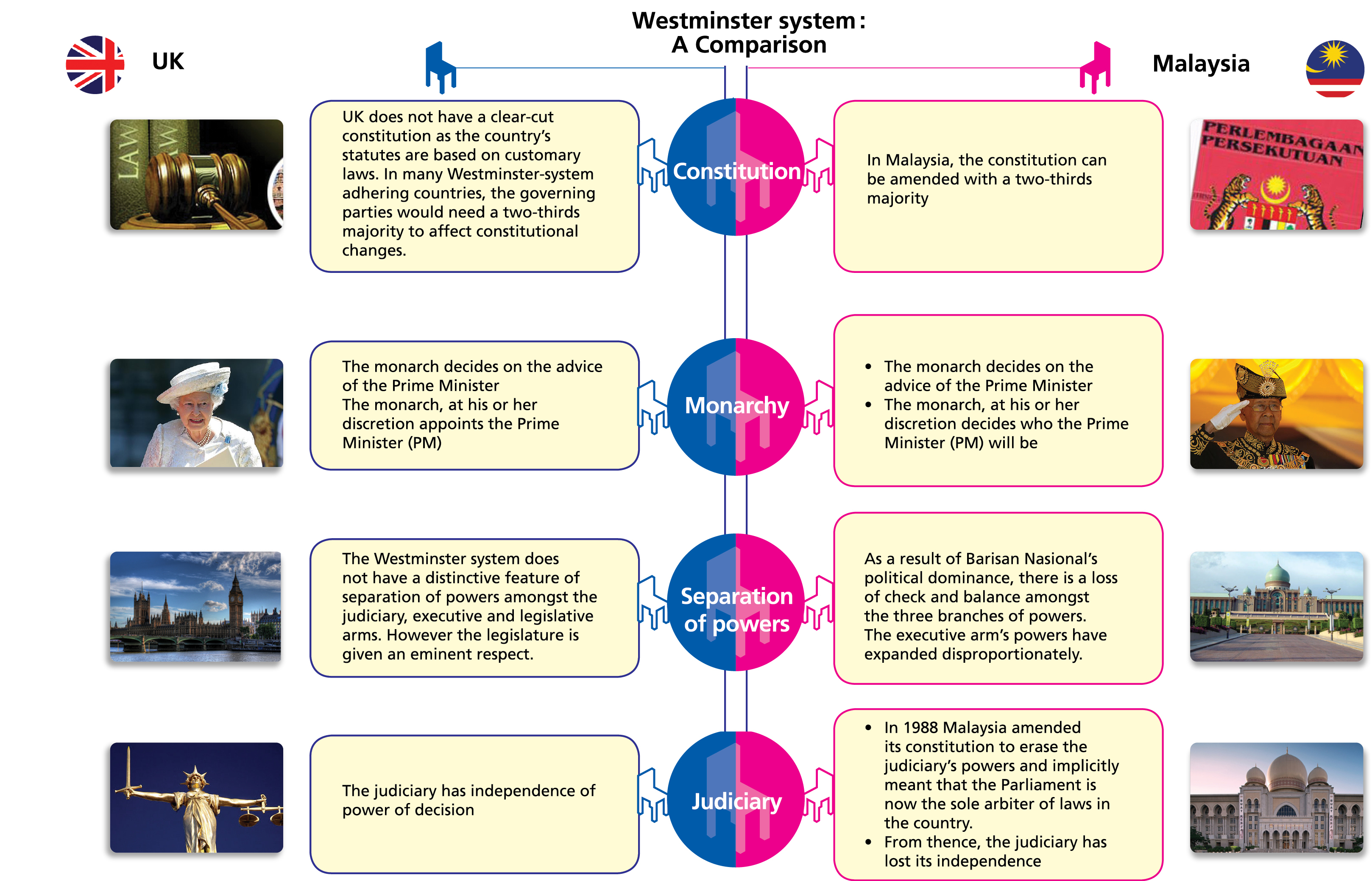
Malaysia was a Federation of 13 States similar to other Federations such as the US and Australia. Its government system closely resembles the Westminster parliamentary system while the jurisdictions of the country are based on the common law. As a former British colony Malaysia has inherited the British Westminster model of parliamentary system and is also a member of the Commonwealth.
Lets look at the hierarchical system within this branch of the political system of Malaysia. Malaysia a new nation whose very existence depends on holding disparate ethnic groups in balance is an example of a developing nation whose legislature does influence policy. Information institution Parliamentary democracy system can be defined as a.
Malaysia was declared on 16 September 1963. Burmas parliamentary system explained. Parliamentary systems fall into two categories.
JournalMP publishes articles related to practice and procedure in Houses of Parliament issues pertaining to the Parliamentary affairs involving the functions of Parliament. The parties in the minority serve. Legislative power is vested in the federal.
In 1957 a constitutional monarchy and parliamentary democracy at Federal and State level were formed with the parliamentary system copied from Westminster. Representative s ystem t hat fea tures the fus ion o f executive and. Malaysia practices Parliamentary Democracy and Constitutional Monarchy.
The basic function of the Executive division is to pass and make amendments to existing federal laws while the. This pioneering survey and analysis of the Malaysian parliament carefully documents and interprets the interaction of legislator party and voter in Malaysia. The United Malays National Organization UMNO together with a coalition of political parties known as the National Front BN has held power.
Malaysia is a federal constitutional monarchy. On 22 August 2013. The politics of Malaysia is based on a federal constitutional monarchy in which the King is head of state and the Prime Minister is the head of government.
The titular head of state called the paramount ruler is elected on a rotating basis from among 9 hereditary chiefs of Malaysias 13 states. The Parliamentary system is the system where the representative of each respective area discusses among them regarding any current issues that arise in Malaysia. 3 Disadvantages of parliamentary system of government.
Uncertainty and instability in government. Executive functions are exercised by members of the parliament appointed by the prime minister to the cabinet. The State Legislatures in Singapore Sabah and Sarawak passed resolutions enabling the establishment of Malaysia.
Journal of the Malaysian Parliament JournalMP is an open-access double-blind peer-reviewed journal published annually by the Research and Library Division Parliament of Malaysia. The state is categorized as a representative democracy. The second situation in which the Executive can make laws is when a Proclamation of Emergency is issued by the YDPA.

Human Rights And The Rule Of Law Rule Of Law Education Centre

5 Malaysian Coin Lot Differ Collectible Coins From Asia Etsy World Coins Coin Collecting Traditional Fabric

Negeri Sembilan Royal Family Malaysia Royal Family

Mnemonics For Upsc Cse Memory Trick To Remember Geography Polity History Economy Yo Geography Lessons General Knowledge Book How To Memorize Things

Gear A4 By Emily96pjm Documents Design Arrivals The Arrival

Malaysia S Longest Ruling Party Seems Set To Return To Prime Minister
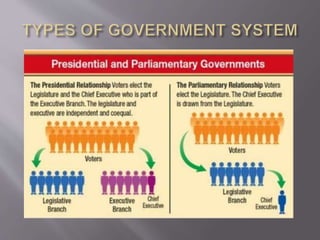
Parliament And Structure Of Federal Government

The Revolution In Russian Military Decision Making Jamestown Decision Making Military Operations Military

The Great Indian Divide Rich In India Versus Poor In India Infographic Indian History Facts Ancient History Facts Indian History

The Constitution Of Malaysia Constitutional Systems Of The World Andrew Harding Hart Publishing

Child Marriage In Malaysia Right To Education Career Counseling Act For Kids

Parliament Of Malaysia Historic Buildings Malaysia Building

Malaysia Just Got A New King Under A Unique System Where 9 Royal Families Take Turns To Rule For 5 Years Each